Keep some notes for understanding the conceptual models built by previous researchers towords game experience.
Experiential Cycle of PX
The experiential cycle describes the UX process between a gamer and a game, the congnitive cycle and aspects relate to the PX.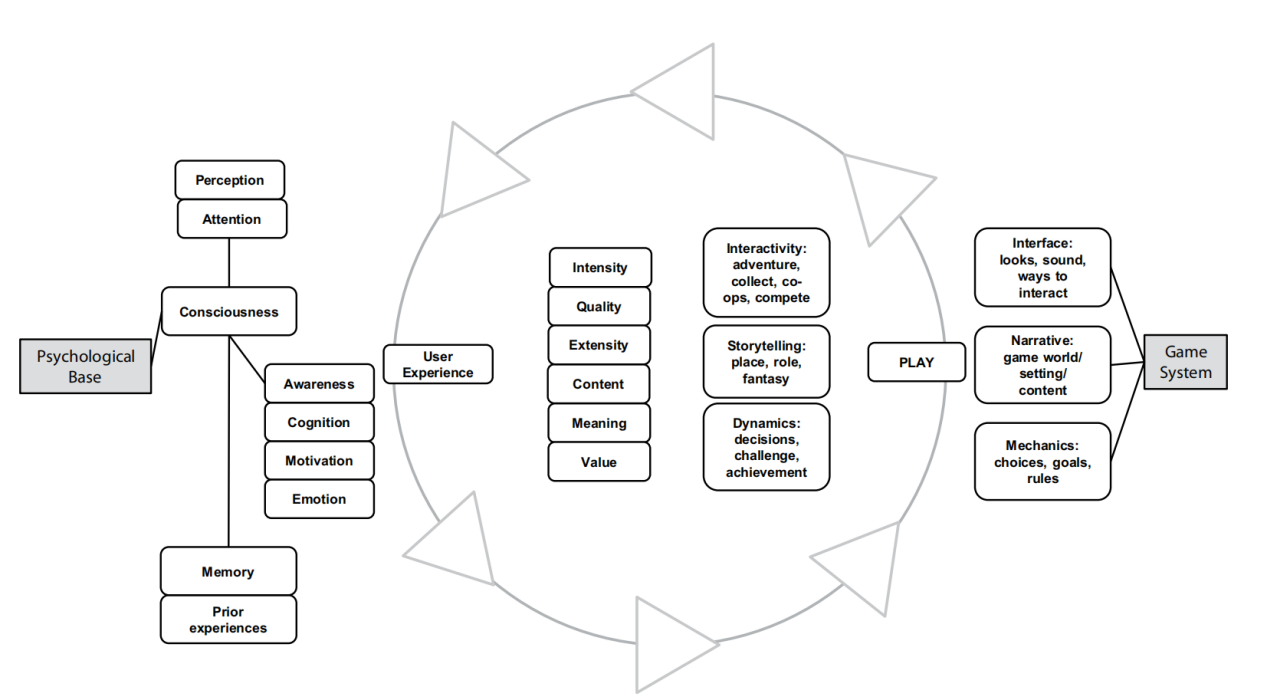
PIFF2 model
This model provides an integrated single framework. Although it is based on the wider concepts of presence, involvement, and flow, PIFF2 aims at understanding the subcomponents of “being there” and “optimal experience”, for example, when playing games.Theoretically PIFF2 is founded on previous studies conducted in the field of game research, while it takes into consideration the way the game content, that is, fundamental game components (i.e., the mechanics, the narrative, and the interface) orient the basic psychological base. Methodologically it is based on a large multivariate data set that is psychometrically analyzed in order to establish a reliable and valid set of subcomponents. These analyses have provided 15 subcomponents for analyzing the UX in games. These subcomponents disclose the content, quality, meaning, value, intensity, and extensity of the UX.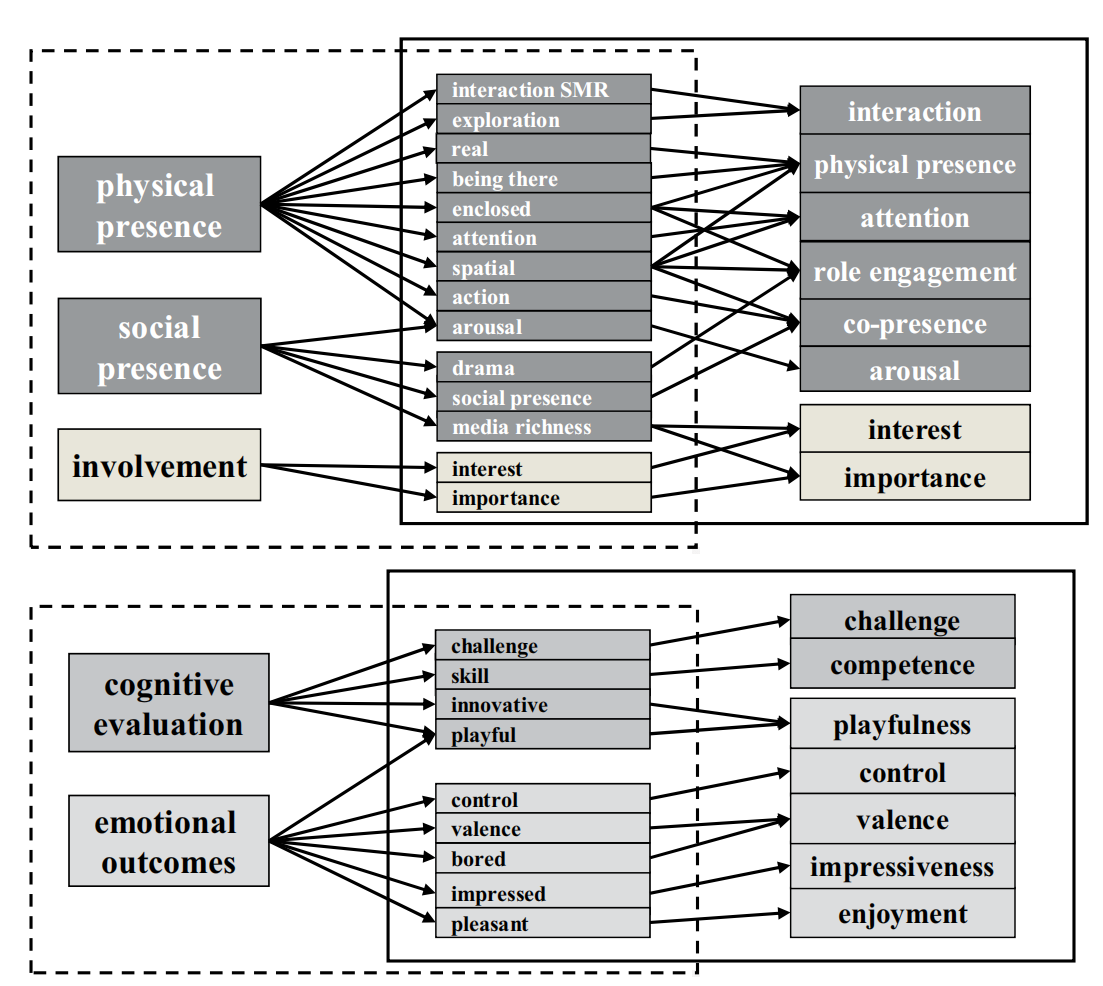
CEGE Model
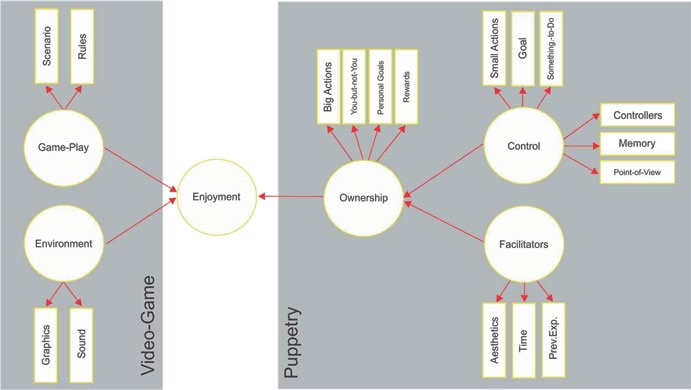
The theory can be summarised in the following three points:
- A positive experience (enjoyment) while playing games is achieved by the player’s perception of the video-game and the interaction with it. These are the Core Elements of the Gaming Experience: Video-game and Puppetry.
- Puppetry, the player’s interaction with the game is formed by the player’s sense
of control and ownership. Control produces ownership, which in turns produces
enjoyment. Ownership is also produced by Facilitators to compensate the sense
of control. - The player’s perception of the video-game is formed by the environment and the
game-play, which also produces enjoyment.
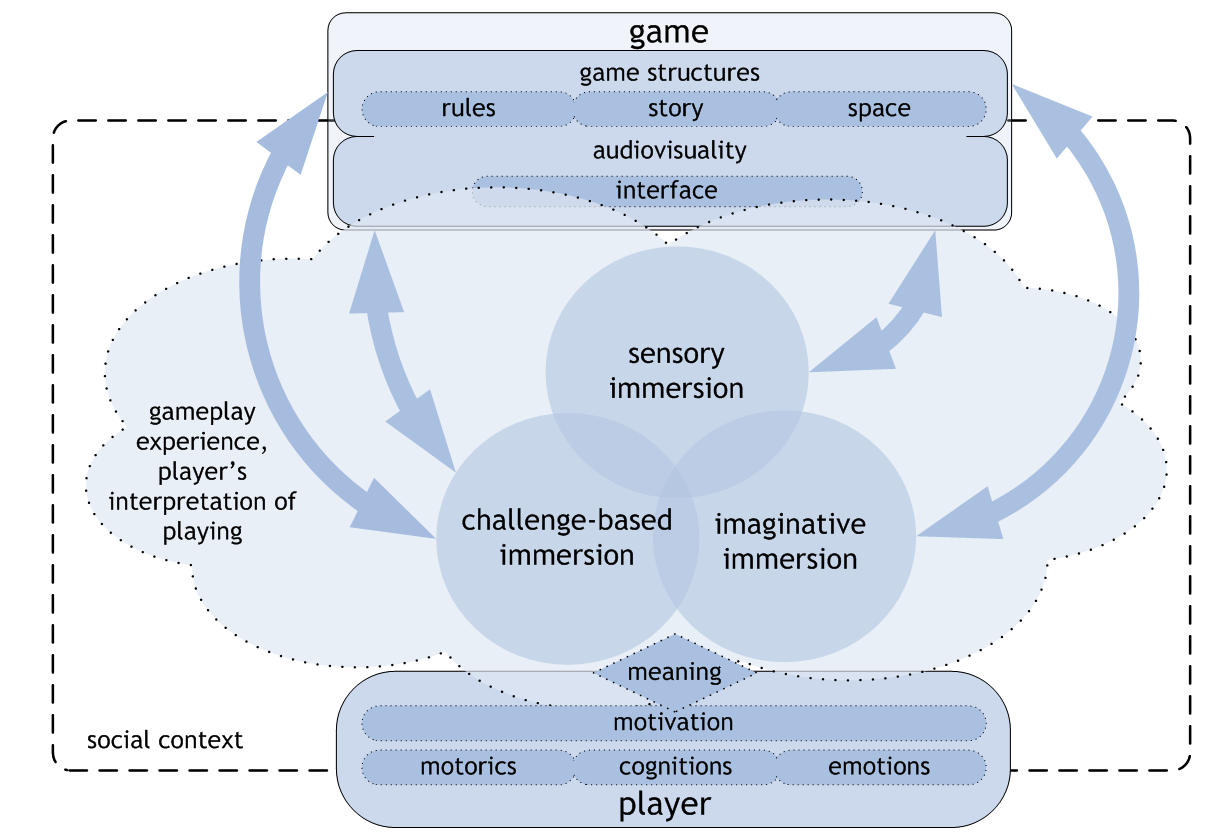
SCI Model
- The first dimension of a gameplay experience that we distinguish is the sensory immersion
related to the audiovisual execution of games. This is something that even those with less experience with games – like the parents of the children that were interviewed – can recognize:
digital games have evolved into audiovisually impressive, three-dimensional and stereophonic worlds that surround their players in a very comprehensive manner. Large screens close to
player’s face and powerful sounds easily overpower the sensory information coming from the
real world, and the player becomes entirely focused on the game world and its stimuli. - Another form of immersion that is particularly central for games, as they are fundamentally
based on interaction, is challenge-based immersion. This is the feeling of immersion that is at its most powerful when one is able to achieve a satisfying balance of challenges and abilities.Challenges can be related to motor skills or mental skills such as strategic thinking or logical
problem solving, but they usually involve both to some degree. - In several contemporary games also the worlds, characters and story elements have become very
central, even if the game would not be classifiable as an actual role-playing game. We call this
dimension of game experience in which one becomes absorbed with the stories and the world, or
begins to feel for or identify with a game character, imaginative immersion. This is the area in which the game offers the player a chance to use her imagination, empathise with the characters,
or just enjoy the fantasy of the game.
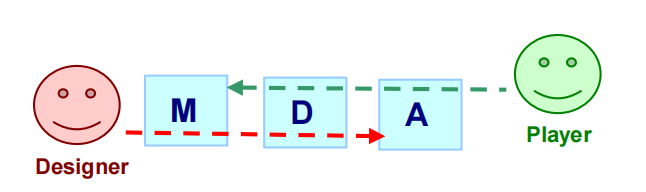
MDA Model
Mechanics describes the particular components of the game, at the level of data representation and algorithms.
Dynamics describes the run-time behavior of the mechanics acting on player inputs and each othersí outputs over time.
Aesthetics describes the desirable emotional responses evoked in the player, when she interacts with the game system.